Run Serverside Google Optimize Tests With Cloudflare Workers
Google Optimize server side experiments are a great way to run A/B tests for free.
The problem?
They’re really slow. Really really slow.
Cloudflare Workers are a way to make them faster with essentially zero code changes to your website.
Very quickly, how this works:
With Google Optimize (the normal version), there are two round trips:
- Your visitor gets your page from your website
- That page is then updated by Google Optimize
The result, your user is waiting around.
The alternative is Cloudflare workers. This Cloudflare worker randomly assigns users for their A/B experience.
Set up steps
Create your Google Optimize experiment
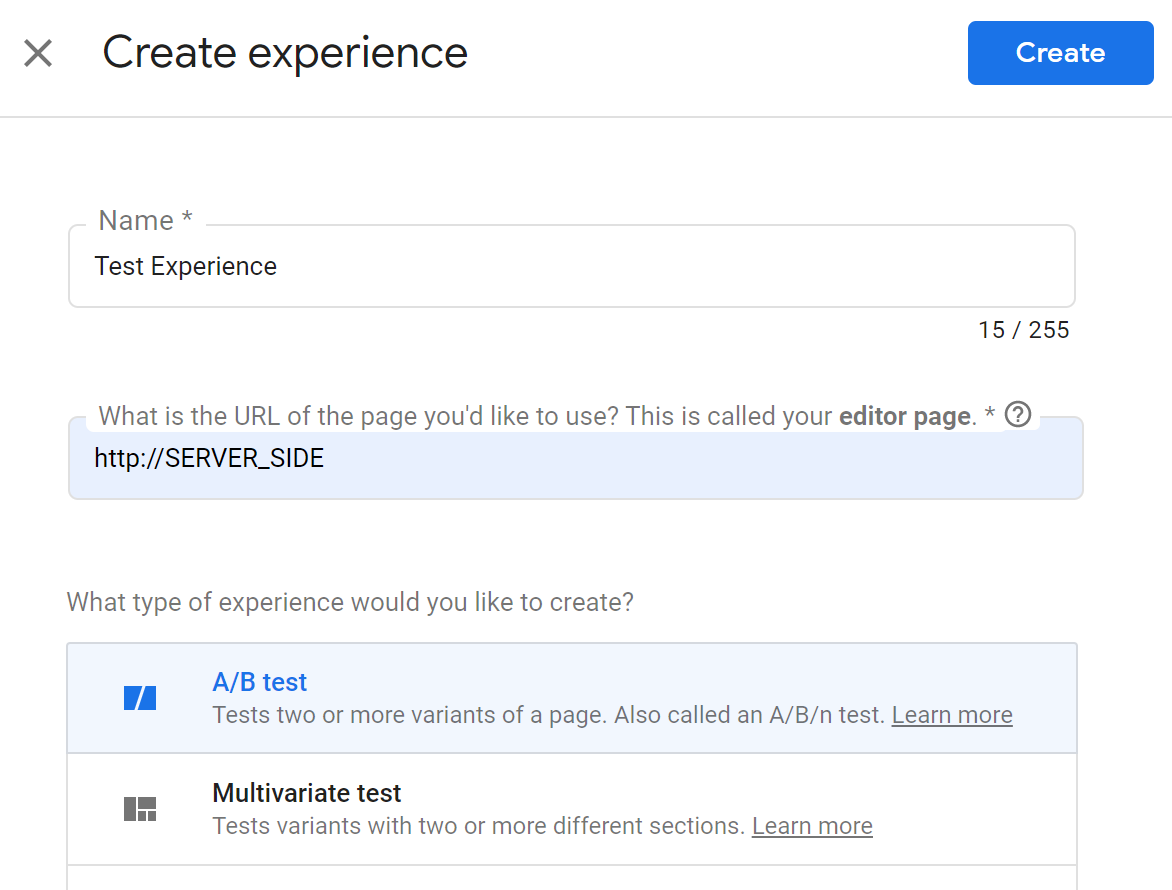
The name doesn’t matter, but be sure to select “A/B” test.
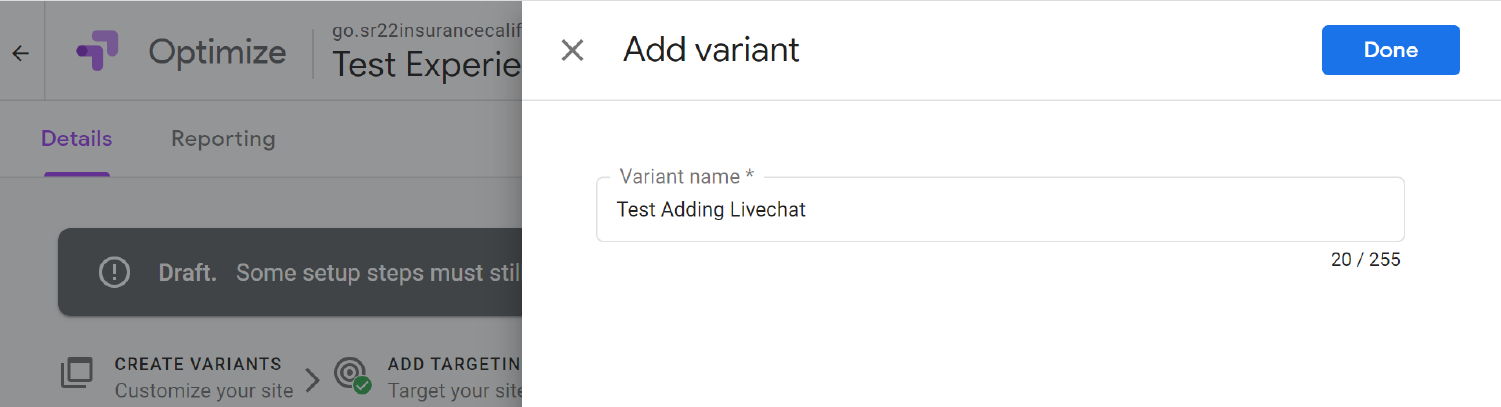
Add a variant
Your dashboard should look something like this:
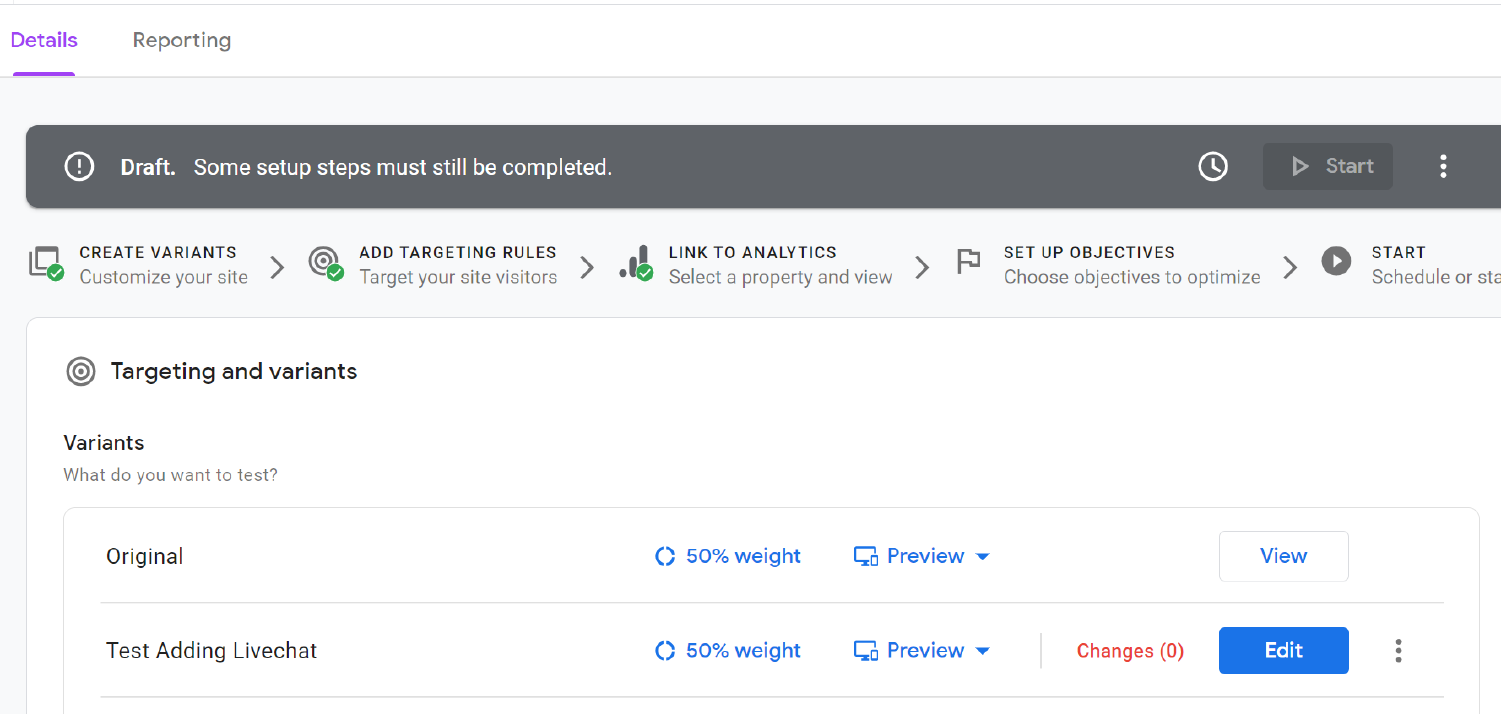
To let Google Optimize know that your experiment is run serverside, click on the pencil
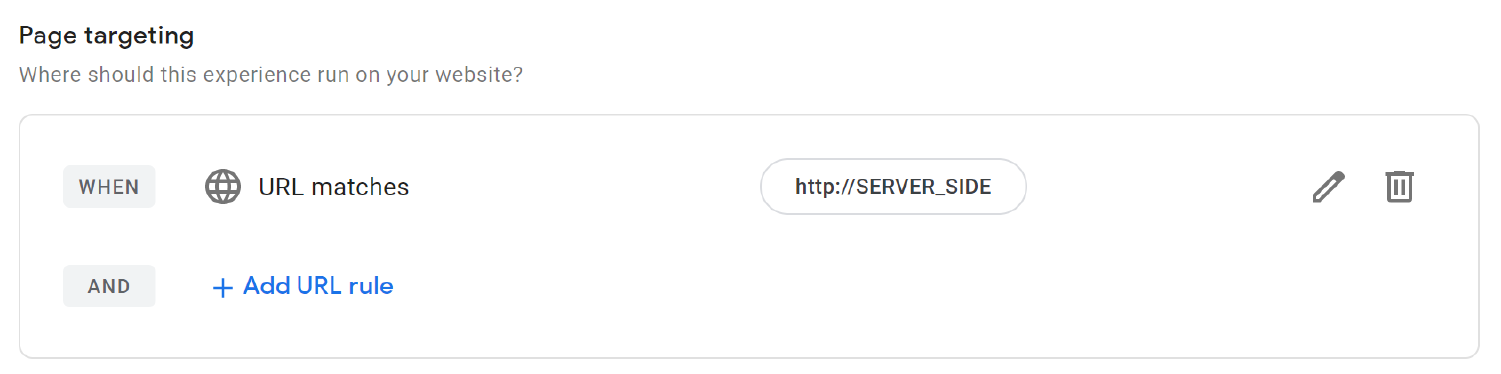
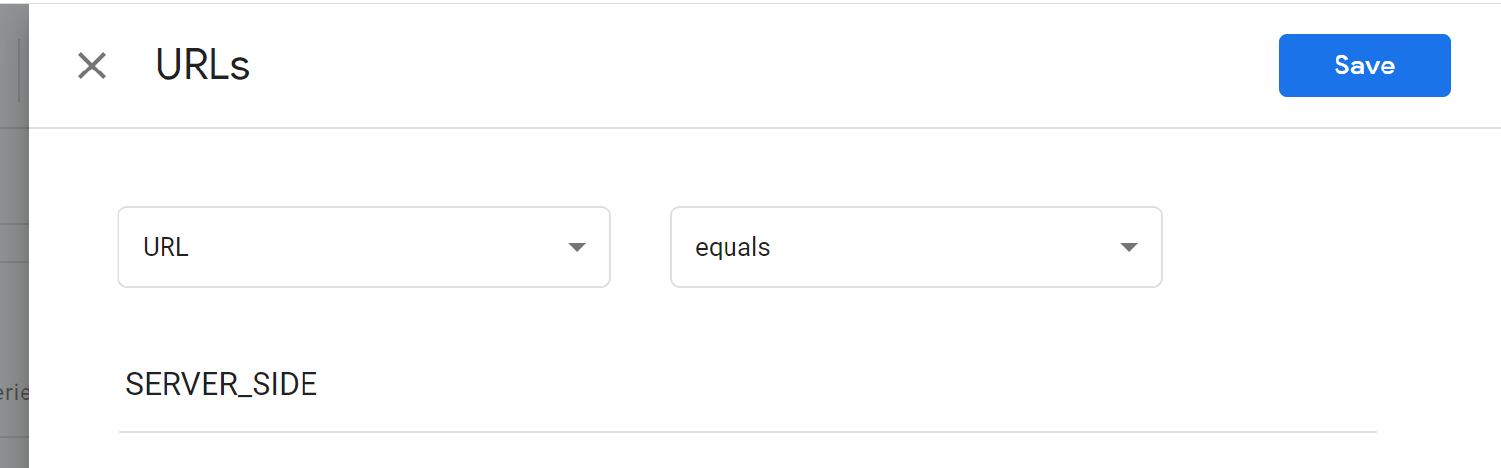
And then update the URL to SERVER_SIDE
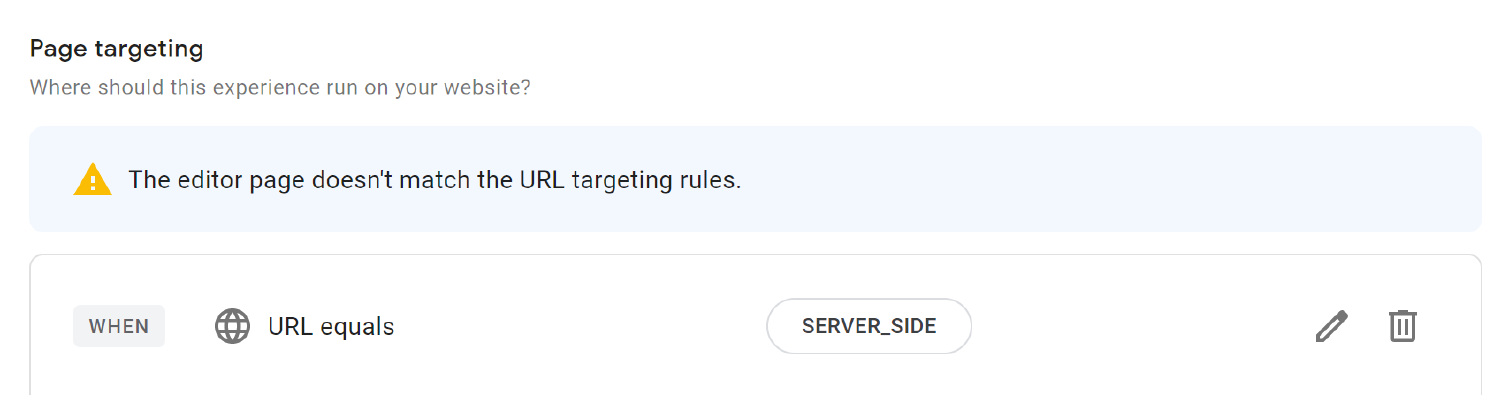
You can ignore this warning.
Copy your experiment ID and then start the experiment.
Update your analytics implementation to work with server side Google Optimize tests
For UA, you need to update the implmentation of your gtag.
For GA4, you’ll send a separate event.
Before:
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag() {
dataLayer.push(arguments);
}
gtag("js", new Date());
gtag("config", "GA_MEASUREMENT_ID");Universal Analytics
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag() {
dataLayer.push(arguments);
}
gtag("js", new Date());
if(window.experimentID && window.experimentVariation){
gtag("config", "GA_MEASUREMENT_ID",
{ experiments:
[{id: window.experimentID, variant: window.experimentVariation}]
});
}) else {
gtag("config", "GA_MEASUREMENT_ID");
}GA4
In GA4, you need to send an event like so:
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag() {
dataLayer.push(arguments);
}
gtag("js", new Date());
gtag("config", "GA_MEASUREMENT_ID");
if(window.experimentID && window.experimentVariation){
gtag('event', 'experiment_impression', {
'experiment_id': window.experimentID,
'variant_id': experimentVariation,
'send_to': 'GA_MEASUREMENT_ID',
});
})
The Code
Get started with Cloudflare workers here
// This is the entrypoint to a Cloudflare worker.
// It just tells Cloudflare to apply a function to someone's request.
addEventListener("fetch", (e) => {
e.respondWith(abExperiment(e.request));
});
// Here is where you configure your experiments
// you can have multiple experiments running simultaneously
const experiments = [
{
expPath: "/path-a", // Run the experiment if a user comes to this path
experimentID: "spt_aLgkQjeC0iHlUe-0WA",
// Each variation is given a path and some details
variants: [
{
path: "/path-a",
// this key is set as a cookie, so future visits are consistent
key: "control",
// user's are bucketed to different experiences using a random number
// generation between 0 and 1.
// In this example, if that number is between .5 and 1, the user will
// get this variation.
//
// You can control the likelihood of a user getting a variation with
// these variables
likelihoodStart: 0.5,
likelihoodEnd: 1,
// The experiment variation is just the variant's index in this variant array
// I chose to be explicit (rather than just grabbing the index)
// for flexibility of changing the variant array
experimentVariation: 0,
},
{
path: "/path-b",
key: "full-page-variant",
likelihoodStart: 0,
likelihoodEnd: 0.5,
experimentVariation: 1,
},
],
},
] as experiments[];
export async function abExperiment(request: Request) {
let requestURL = new URL(request.url);
// To start, not every request should run an experiment. This
// filters out tests
if (!shouldRunExperiment(requestURL.pathname)) {
// this caches your content so subsequent requests are very
// vast
return fetch(requestURL.toString(), {
cf: {
cacheTtl: 6000000,
cacheEverything: true,
},
});
}
// This gets the experiment ID and variation
// It's wrapped in a try/catch block just in case
// something goes wrong with your configuration
let experimentID = "";
let experimentVariation = {} as variant;
try {
const experimentVariables = getExperimentVariables(requestURL.pathname);
experimentVariation = getExactExperimentData(experimentVariables);
experimentID = getExperimentID(requestURL.pathname);
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
return new Response(e as string);
}
// Update the URL to include the experiment subdirectory, if applicable.
const resourceURL = new URL(
[requestURL.origin, experimentVariation.path, requestURL.search].join("")
);
// This fetches the page of your experiment
const res = await fetch(resourceURL.toString(), {
cf: {
cacheTtl: 6000000,
cacheEverything: true,
},
});
const contentType = res.headers.get("Content-Type");
// If the response is HTML, it can be transformed with
// HTMLRewriter -- otherwise, it should pass through
if (contentType?.startsWith("text/html")) {
return new HTMLRewriter()
.on(
"head",
new ElementHandler(
experimentVariation.experimentVariation,
experimentID
)
)
.transform(res);
} else {
return res;
}
}
class ElementHandler {
private experimentVariation: number;
private experimentID: string;
constructor(experimentVariation: number, experimentID: string) {
this.experimentVariation = experimentVariation;
this.experimentID = experimentID;
}
// this simple handler just sets the global variables for the experiment ID and
// experiment variation
element(element: any) {
element.append(
`
<script>
window.experimentID = '${this.experimentID}'
window.experimentVariation = '${this.experimentVariation}'
</script>
`,
{ html: true }
);
}
}
type experiments = {
expPath: string;
variants: variant[];
experimentID: string;
};
type variant = {
path: string;
key: string;
likelihoodStart: number;
likelihoodEnd: number;
experimentVariation: number;
};
// shouldRunExperiment matches paths in the experiment object
export const shouldRunExperiment = (path: string): boolean => {
let shouldRun = false;
experiments.forEach((exp) => {
if (path == exp.expPath) {
shouldRun = true;
}
});
return shouldRun;
};
// getExperimentVariables returns the first matching variable
// the error condition technically should never be reached, but
// who know's how you're going to change this ;)
export const getExperimentVariables = (path: string): variant[] => {
for (let i = 0; i < experiments.length; i++) {
if (experiments[i].expPath == path) {
return experiments[i].variants;
}
}
throw new Error("no matching variables");
};
// getExperimentID loops and gets the experimentID from the given path
export const getExperimentID = (path: string): string => {
for (let i = 0; i < experiments.length; i++) {
if (experiments[i].expPath == path) {
return experiments[i].experimentID;
}
}
throw new Error("no experiment ID");
};
// getExactExperimentData generates a random number to get a random
// experience based on the odds you set.
export const getExactExperimentData = (expValue: variant[]) => {
let randNumber = Math.random();
for (let i = 0; i < expValue.length; i++) {
if (
randNumber > expValue[i].likelihoodStart &&
randNumber < expValue[i].likelihoodEnd
) {
return expValue[i];
}
}
throw new Error("no matching experiment");
};